OpenVAS began in 2005 when Nessus transitioned from open source to a proprietary license. Two companies, Intevation and DN Systems adopted the existing project and began evolving and maintaining it under a GPL v2.0 license. Since then, OpenVAS has evolved into Greenbone, the most widely-used and applauded open-source vulnerability scanner and vulnerability management solution in the world. We are proud to offer Greenbone as both a free Community Edition for developers and also as a range of enterprise products featuring our Greenbone Enterprise Feed to serve the public sector and private enterprises alike.

As the “old-dog” on the block, Greenbone is hip to the marketing games that cybersecurity vendors like to play. However, our own goals remain steadfast – to share the truth about our product and industry leading vulnerability test coverage. So, when we reviewed a recent 2024 network vulnerability scanner benchmark report published by a competitor, we were a little shocked to say the least.
As the most recognized open-source vulnerability scanner, it makes sense that Greenbone was included in the competition for top dog. However, while we are honored to be part of the test, some facts made us scratch our heads. You might say we have a “bone to pick” about the results. Let’s jump into the details.
What the 2024 Benchmark Results Found
The 2024 benchmark test conducted by Pentest-Tools ranked leading vulnerability scanners according to two factors: Detection Availability (the CVEs each scanner has detection tests for) and Detection Accuracy (how effective their detection tests are).
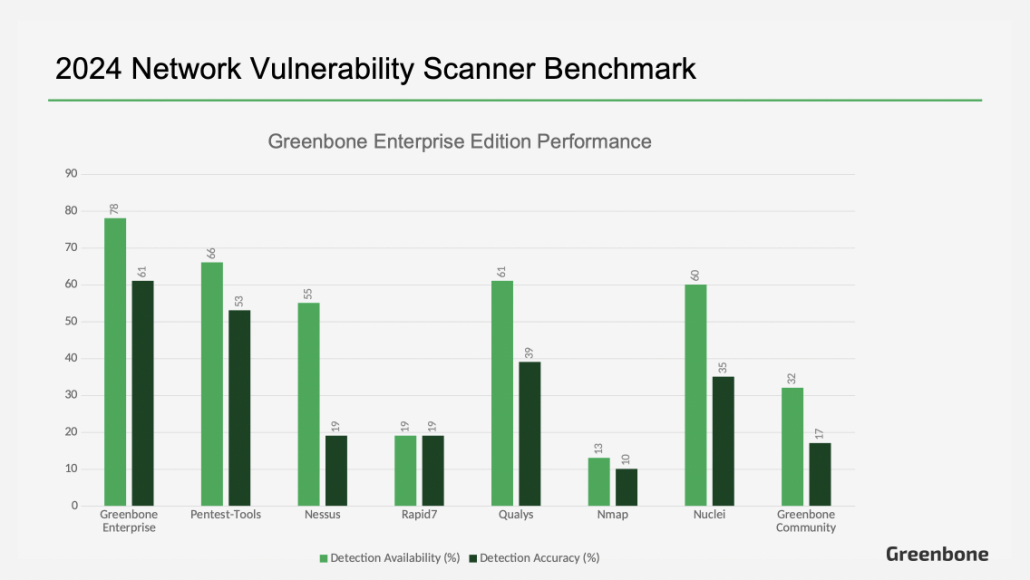
The benchmark pitted our free Community Edition of Greenbone and the Greenbone Community Feed against the enterprise products of other vendors: Qualys, Rapid7, Tenable, Nuclei, Nmap, and Pentest-Tools’ own product. The report ranked Greenbone 5th in Detection Availability and roughly tied for 4th place in Detection Accuracy. Not bad for going up against titans of the cybersecurity industry.
The only problem is, as mentioned above, Greenbone has an enterprise product too, and when the results are recalculated using our Greenbone Enterprise Feed, the findings are starkly different – Greenbone wins hands down.
Here is What we Found
Our Enterprise Feed Detection Availability Leads the Pack
According to our own internal findings, which can be verified using our SecInfo Portal, the Greenbone Enterprise Feed has detection tests for 129 of the 164 CVEs included in the test. This means our Enterprise product’s Detection Availability is a staggering 70.5% higher than reported, placing us heads and tails above the rest.
To be clear, the Greenbone Enterprise Feed tests aren’t something we added on after the fact. Greenbone updates both our Community and Enterprise Feeds on a daily basis and we are often the first to release vulnerability tests when a CVE is published. A review of our vulnerability test coverage shows they have been available from day one.
Our Detection Accuracy was far Underrated
And another thing. Greenbone isn’t like those other scanners. The way Greenbone is designed gives it strong industry leading advantages. For example, our scanner can be controlled via API allowing users to develop their own custom tools and control all the features of Greenbone in any way they like. Secondly, our Quality of Detection (QoD) ranking doesn’t even exist on most other vulnerability scanners.
The report author made it clear they simply used the default configuration for each scanner. However, without applying Greenbone’s QoD filter properly, the benchmark test failed to fairly assess Greenbone’s true CVE detection rate. Applying these findings Greenbone again comes out ahead of the pack, detecting an estimated 112 out of the 164 CVEs.
Summary
While we were honored that our Greenbone Community Edition ranked 5th in Detection Availability and tied for 4th in Detection Accuracy in a recently published network vulnerability scanner benchmark, these results fail to consider the true power of the Greenbone Enterprise Feed. It stands to reason that our Enterprise product should be in the running. Afterall, the benchmark included enterprise offerings from other vendors.
When recalculated using the Enterprise Feed, Greenbone’s Detection Availability leaps to 129 of the 164 CVEs on the test, 70.5% above what was reported. Also, using the default settings fails to account for Greenbone’s Quality of Detection (QoD) feature. When adjusted for these oversights, Greenbone ranks at the forefront of the competition. As the most used open-source vulnerability scanner in the world, Greenbone continues to lead in vulnerability coverage, timely publication of vulnerability tests, and truly enterprise grade features such as a flexible API architecture, advanced filtering, and Quality of Detection scores.